
Ĭaution needs to be exercised, in particular, with retrospective cohort studies because errors due to confounding and bias are more common in retrospective studies than in prospective studies. Retrospective studies examine possible risk and protection variables in relation to a result that is already established at the start of the study. The time to complete a retrospective study is only as long as it takes to collect and interpret the data. It is important to understand that the methodology of prospective and retrospective cohort studies is fundamentally the same, but the retrospective study is performed post-hoc, as the cohort is followed retrospectively.
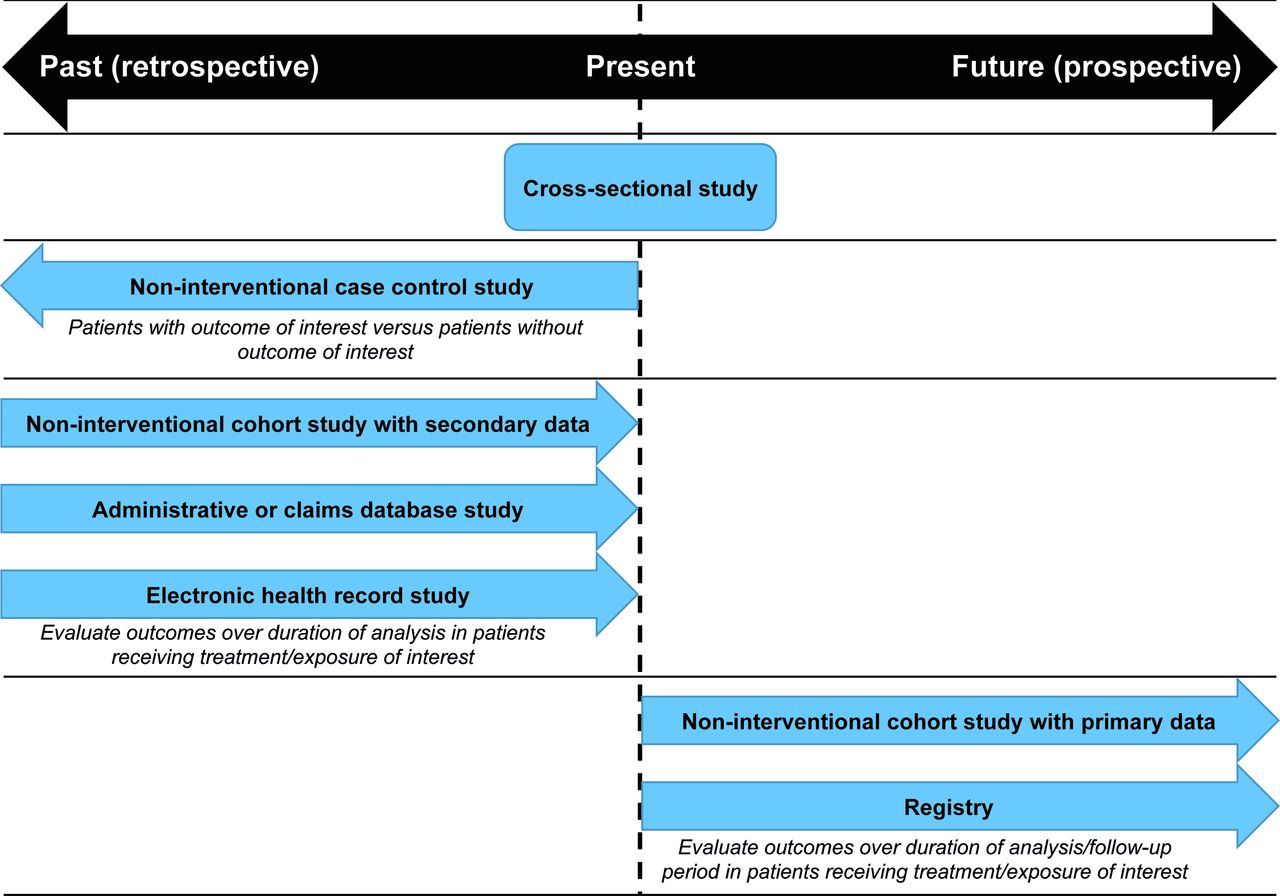
On the other hand, Prospective Cohort Study is conducted by starting with two groups at the current point, and following up in future for occurrence of disease, if any. We merely collect the data now, and establish the risk of developing a disease if exposed to a particular risk factor. development of disease) have already occurred in the past. In a nutshell, in Retrospective Cohort Study, all the events - exposure, latent period, and subsequent outcome (ex. The first objective is still to establish two groups - exposed versus non-exposed and these groups are followed up in the ensuing time period. However, the starting point of this study is the same as for all cohort studies. In the case of a retrospective cohort study, the investigator collects data from past records and does not follow patients up as is the case with a prospective study.

In retrospective cohort studies, a risk ratio or odds ratio gives an assessment of relative risk. It is a medical and psychological research study in which the records of groups of individuals who are alike in many ways but differ by a certain characteristic (for example, female nurses who smoke and those who do not smoke) are compared for a particular outcome (such as lung cancer). Retrospective cohort studies have existed for approximately as long as prospective cohort studies. A retrospective cohort study, also called a historic cohort study, is a longitudinal cohort study that studies a cohort of individuals that share a common exposure factor to determine its influence on the development of a disease, and are compared to another group of equivalent individuals that were not exposed to that factor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
